How Does Glutamate Work In The Body
Table of Contents
Introduction
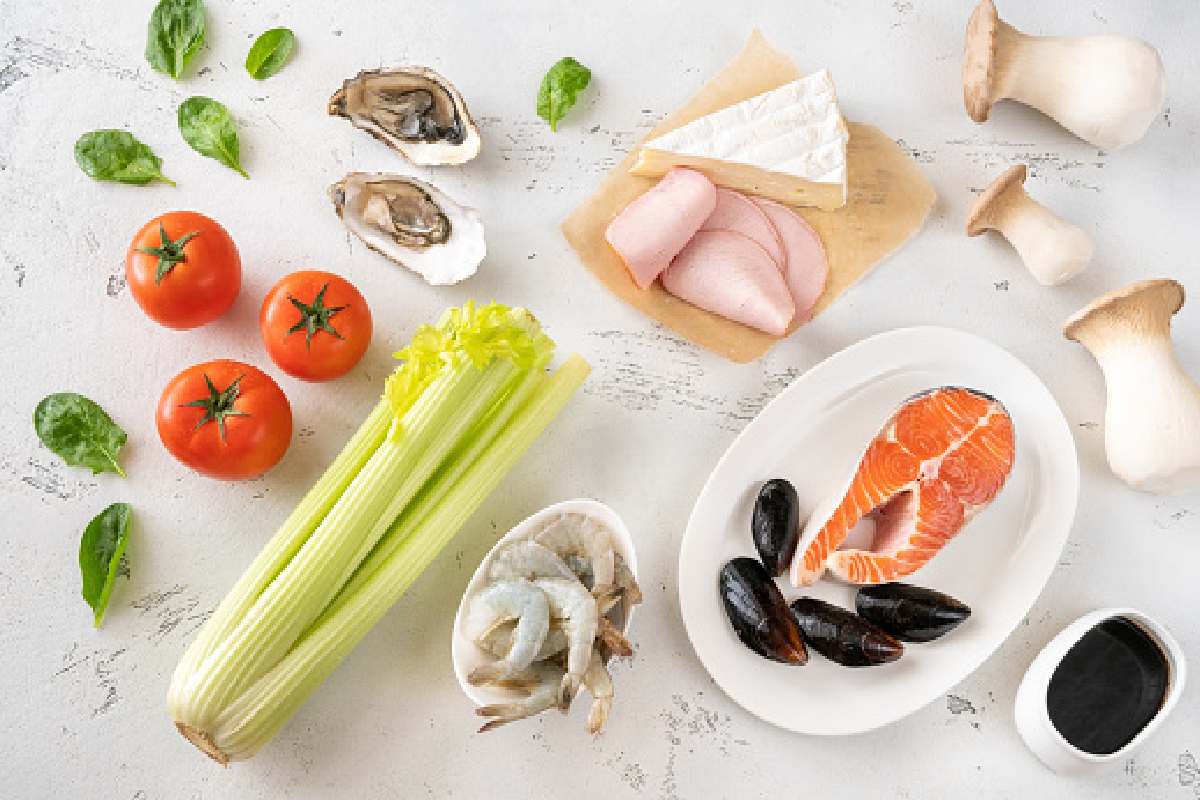
In its original form, glutamate is determined in meals and fish, meat, and tomatoes. It is likewise a critical messenger substance that the frame produces itself. However, glutamate is also frequently observed in gear-up meals and crisps as an additive E 621. Some time ago, the suspicion arose that too much of it promotes anxious sicknesses. Is that accurate? Read more extraordinary about glutamate.
In your brain, glutamate remains the most rich excitatory neurotransmitter. The excitant neurotransmitter stimulates the nerve cell, making it more likely that the chemical message will continue to travel from nerve cell to courage cell rather than being. Glutamate is essential for proper brain function.
Glutamate: what is it?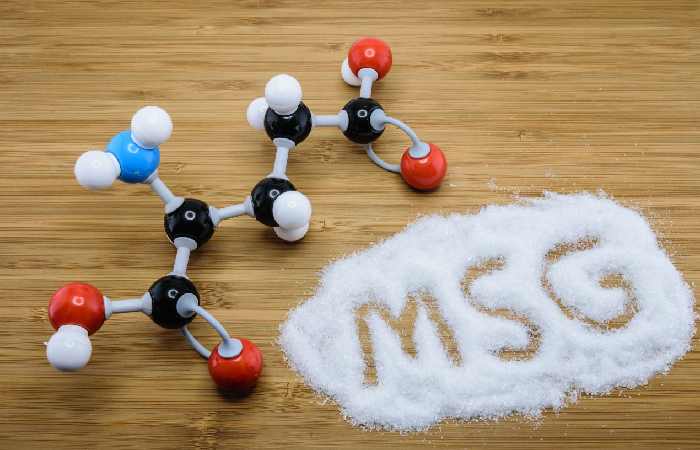
The Glutamate is a salt of glutamic cutting, an amino acid, and it is determined clearly in all protein compounds. The body can produce itself (endogenous glutamate). However, we additionally ingest glutamate through herbal foods and the taste enhancer E 621 (exogenous glutamate).
Exogenous glutamate is mainly found in protein-wealthy meals, including meat and fish. But it is also found in dairy products and plenty of greens, including tomatoes.
In addition, the meals enterprise has remains producing the flavour enhancer monosodium glutamate since the start of the twentieth century, and it is likewise called sodium salt. Monosodium glutamate remains formed utilizing the chemical response of glutamic acid and sodium carbonate (E500) or sodium hydroxide.
Monosodium glutamate is likewise call E 621. The additive stands for the fifth flavour, “umami,” which is “spicy and tasting a little like broth.” Seasoning remains often used in finish products.
How does glutamate paintings within the frame?
Glutamate plays a crucial function within the body. It is an essential neurotransmitter inside the relevant anxious machine and permits signalling between cells. It affects the subsequent capabilities:
- pain transmission
- frame growth
- weight law
- appetite law
Too much endogenous glutamate can result in mind cells’ demise within the mind, mainly to illnesses including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s sickness, and a couple of cases of sclerosis.
However, it’s miles not likely that glutamates from meals will move the brain-blood barrier and reach the brain. When consuming, the frame absorbs each herbal glutamate and monosodium glutamate nicely and metabolizes each bureaucracy completely.
Is it risky?
Glutamic acid is regularly associate with “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome.” After eating meals that incorporate glutamate as an additive, the affecte generally complain of headaches and body aches, numbness inside the neck, and nausea.
However, this thesis has now not remained scientifically shown. The signs and symptoms occasionally appear while someone consumes extra than ten grams in a speedy time. However, such quantities are practically inconceivable thru the intake of food.
It is believe that the signs and symptoms in people who are predispose to this are prompte by using other materials such as histamine.
Neither technology nor country authorities could prove that poses a fitness hazard, and it’s far considere innocent. Within the EU, E 621 is a tested and accredited additive.
However, it has to be mentione that a condiment regularly stimulates the appetite and promotes resistance to the “satisfaction” hormone leptin. Therefore, there is a danger that you’ll advantage weight through the common intake of foods with E 621, which will lead to unhealthy weight problems.
Where is use?
Food manufacturers use monosodium to atone for the loss of taste that necessarily takes place while dehydrating, cooking, or in any other case processing ready meals. Without it, many (semi) ready meals would be flavour bland.
Of all the accredite glutamates, E 621 is the maximum use inside the food enterprise, regularly together with desk salt, guanylates (E 626), or inosinates (E 630).
In the European Union, some decide how monosodium maybe introduce to meals. A most of ten grams in line with the kilogram of the respective product applies. In the case of ready-to-eat meals, the addition should be diagnose by observing a “flavour enhancer” in the list of ingredients.
It is typically determine inside the following meals:
- frozen ready meals
- canned/dry meals
- spice blends
- salad dressings
- Natural is likewise determine, as an instance, in:
- tomatoes
- Parmesan
- bird egg
- meat
- yeast extract
Monosodium glutamate and yeast extract – what is the difference?
Yeast extract additionally consists of approximately five per cent. Nevertheless, monosodium [glutamate] and yeast extract aren’t identical. While the mass-produced is an isolated pure substance, yeast extract consists of amino acids, proteins, nutrients, minerals, and salt in addition to.
Yeast extract also acts as a flavour enhancer but should no longer be declare as such because is present.

